i second that :razz: i would love to come and see your pond when u have it up and running all the hard work u and your family have put in to it makes it worth the trip :-P
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
WHISKEYS NEW POND PROJECT
- Thread starter whiskey
- Start date
whiskey
Always trying to perfect something fishy
- Joined
- Jun 23, 2010
- Messages
- 45,120
- Reaction score
- 30,190
- Location
- Frederick, Maryland
- Showcase(s):
- 1
- Hardiness Zone
- 6b
- Country

lol so fill your pond as it rains...........they will think the rain did it!
j.w
I Love my Goldies
- Joined
- Feb 1, 2010
- Messages
- 34,099
- Reaction score
- 20,977
- Location
- Arlington, Washington
- Showcase(s):
- 1
- Hardiness Zone
- USDA 8a
- Country

Was wondering how they know when you are using your hose whiskey? Do you have a meter on it or do neighbors just rat on ya?
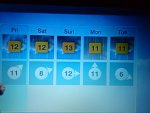
where did u hear thayy a hosepipe ban 1st iv heard of itHi to one and all,
weather holding every thing up .......see next few days on photo......rain .rain..rain. rain ....and we got a hose pipe ban.....as the TV show" mrs brown boys" would say THATS NICE
whiskey
Always trying to perfect something fishy
Hello,
Been awhile now, managed two mornings of blocking, during last couple of days, before the rain sets in and spoils rest of day.
Built the right hand side of window support plus a few blocks along deck walk.
I know its April but two morning out of 13 days, enough enough of rain wind and more rain forecast until thursday.
A few photo of build.
whiskey
Been awhile now, managed two mornings of blocking, during last couple of days, before the rain sets in and spoils rest of day.
Built the right hand side of window support plus a few blocks along deck walk.
I know its April but two morning out of 13 days, enough enough of rain wind and more rain forecast until thursday.
A few photo of build.
whiskey
Attachments
j.w
I Love my Goldies
- Joined
- Feb 1, 2010
- Messages
- 34,099
- Reaction score
- 20,977
- Location
- Arlington, Washington
- Showcase(s):
- 1
- Hardiness Zone
- USDA 8a
- Country

You are one professional pond perfectionist there whiskey!
- Joined
- Jun 23, 2010
- Messages
- 45,120
- Reaction score
- 30,190
- Location
- Frederick, Maryland
- Showcase(s):
- 1
- Hardiness Zone
- 6b
- Country

Very nice
What's rain?
- Joined
- Jun 23, 2010
- Messages
- 45,120
- Reaction score
- 30,190
- Location
- Frederick, Maryland
- Showcase(s):
- 1
- Hardiness Zone
- 6b
- Country

wet stuff that falls from the sky...............
What's rain?
whiskey
Always trying to perfect something fishy
DRIP................... SPRINGS TO MIND
- Joined
- Mar 20, 2011
- Messages
- 7,257
- Reaction score
- 4,819
- Location
- near Effingham, Illinois
- Hardiness Zone
- 5b
Outstanding job, Whiskey! And, I only expected it to be perfectly level, with your expertise! It's coming along very well, despite the rains there. Hope you get some more dry days to work more on it. Great photos. Anxiously waiting for more. 
j.w
I Love my Goldies
- Joined
- Feb 1, 2010
- Messages
- 34,099
- Reaction score
- 20,977
- Location
- Arlington, Washington
- Showcase(s):
- 1
- Hardiness Zone
- USDA 8a
- Country

RAIN for waterbug the nerd all dried up in Az,lol!
Rain is liquid precipitation, as opposed to non-liquid kinds of precipitation such as snow, hail and sleet. Rain requires the presence of a thick layer of the atmosphere to have temperatures above the melting point of water near and above the Earth's surface. On Earth, it is the condensation of atmospheric water vapor into drops of water heavy enough to fall, often making it to the surface. Two processes, possibly acting together, can lead to air becoming saturated leading to rainfall: cooling the air or adding water vapor to the air. Virga is precipitation that begins falling to the earth but evaporates before reaching the surface; it is one of the ways air can become saturated. Precipitation forms via collision with other rain drops or ice crystals within a cloud. Large rain drops are oblate-shaped and small drops are spherical. Moisture moving along three-dimensional zones of temperature and moisture contrasts known as weather fronts is the major method of rain production. If enough moisture and upward motion is present, precipitation falls from convective clouds (those with strong upward vertical motion) such as cumulonimbus (thunderstorms) which can organize into narrow rainbands. In mountainous areas, heavy precipitation is possible where upslope flow is maximized within windward sides of the terrain at elevation which forces moist air to condense and fall out as rainfall along the sides of mountains. On the leeward side of mountains, desert climates can exist due to the dry air caused by downslope flow which causes heating and drying of the air mass. The movement of the monsoon trough, or intertropical convergence zone, brings rainy seasons to savannah climes. Rain is the primary source of freshwater for most areas of the world, providing suitable conditions for diverse ecosystems, as well as water for hydroelectric power plants and crop irrigation. Rainfall is measured via rain gauges. Rainfall amounts can be estimated by weather radar.

Rain is liquid precipitation, as opposed to non-liquid kinds of precipitation such as snow, hail and sleet. Rain requires the presence of a thick layer of the atmosphere to have temperatures above the melting point of water near and above the Earth's surface. On Earth, it is the condensation of atmospheric water vapor into drops of water heavy enough to fall, often making it to the surface. Two processes, possibly acting together, can lead to air becoming saturated leading to rainfall: cooling the air or adding water vapor to the air. Virga is precipitation that begins falling to the earth but evaporates before reaching the surface; it is one of the ways air can become saturated. Precipitation forms via collision with other rain drops or ice crystals within a cloud. Large rain drops are oblate-shaped and small drops are spherical. Moisture moving along three-dimensional zones of temperature and moisture contrasts known as weather fronts is the major method of rain production. If enough moisture and upward motion is present, precipitation falls from convective clouds (those with strong upward vertical motion) such as cumulonimbus (thunderstorms) which can organize into narrow rainbands. In mountainous areas, heavy precipitation is possible where upslope flow is maximized within windward sides of the terrain at elevation which forces moist air to condense and fall out as rainfall along the sides of mountains. On the leeward side of mountains, desert climates can exist due to the dry air caused by downslope flow which causes heating and drying of the air mass. The movement of the monsoon trough, or intertropical convergence zone, brings rainy seasons to savannah climes. Rain is the primary source of freshwater for most areas of the world, providing suitable conditions for diverse ecosystems, as well as water for hydroelectric power plants and crop irrigation. Rainfall is measured via rain gauges. Rainfall amounts can be estimated by weather radar.
j.w
I Love my Goldies
- Joined
- Feb 1, 2010
- Messages
- 34,099
- Reaction score
- 20,977
- Location
- Arlington, Washington
- Showcase(s):
- 1
- Hardiness Zone
- USDA 8a
- Country

Whiskey how long is this project gonna take? Not pushing you, just curious if it will be done by winter time when the rains come................lol!
- Joined
- Mar 20, 2011
- Messages
- 7,257
- Reaction score
- 4,819
- Location
- near Effingham, Illinois
- Hardiness Zone
- 5b
Woohoo, I was able to "like" your description of rain, JW. And, loved the pic of rain, too. LOL
Poor Waterbug, getting no rain, and Whiskey, getting too much like you, JW. We should be able to share our rain with our friends who are not getting enough, and then we would all be happy. Maybe we can put in a request for that .....
Poor Waterbug, getting no rain, and Whiskey, getting too much like you, JW. We should be able to share our rain with our friends who are not getting enough, and then we would all be happy. Maybe we can put in a request for that .....
Ask a Question
Want to reply to this thread or ask your own question?
You'll need to choose a username for the site, which only take a couple of moments. After that, you can post your question and our members will help you out.
Similar Threads
Forum statistics
Latest Threads
-
Cardinal drinking in the stream
- Started by RobAmy
-
Now and then
- Started by RobAmy
-
Algae on plant pots etc
- Started by woodturner with koi
-
Goldfish swelled up like a ball
- Started by ellebea
-
Peat moss in Bog Filter
- Started by drjay9051
-
Bog Build With Settling Chamber
- Started by TurtTown
-
Pond Liner
- Started by nglthomas
-
Algaecide use questions
- Started by BarbAZCA
-
LDPE pond liner, which side should face water
- Started by sherry